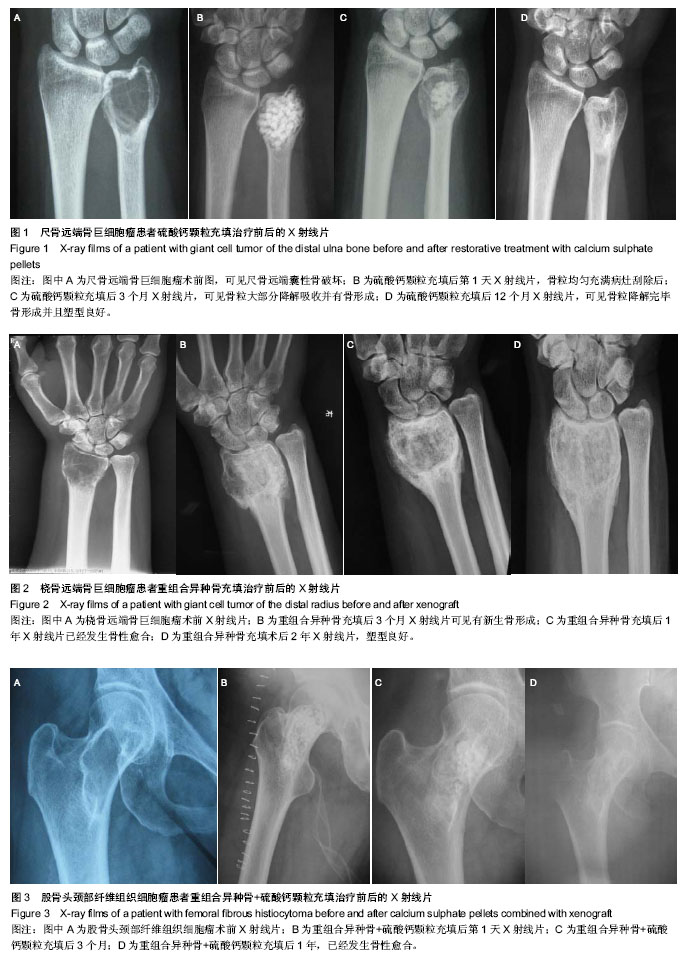
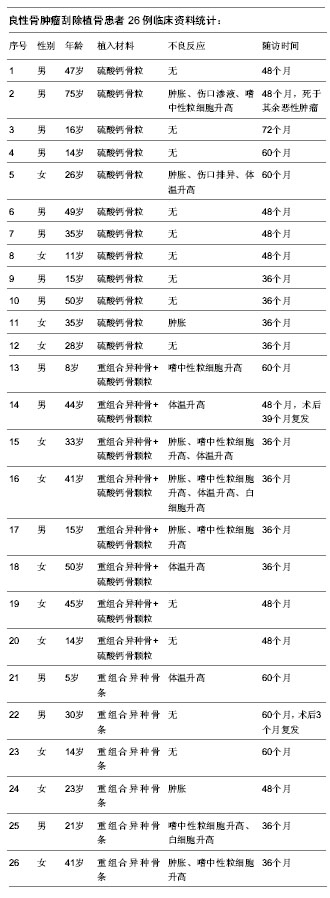
| [1] 袁凯,陈建庭.脊柱结核外科治疗植骨材料的临床应用与研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(21):1957-1959.
[2] Winkler T,Hoenig E,Gildenhaar R,et al. Volumetric analysis of osteoclastic bioresorption of calcium phosphate ceramics with different solubilities.Acta Biomaterialia, 2010; 6:4127-4135.
[3] Van der Stok J,Van Lieshout EM,El-Massoudi Y,et al.Bone substitutes in the Netherlands-A systematic literature review. Acta Biomaterialia.2011;7(2):739-750.
[4] 周长明,张家国,时永臣.人工植骨材料的生物学特性与临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(12): 2225-2228.
[5] 辛雷,苏佳灿.人工骨修复材料的现状与展望[J].创伤外科杂志, 2011,13(3):272-275.
[6] 郝强,赵丽,关继奎,等.人工骨材料在骨缺损修复中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(34):6745-6748.
[7] 陈东,张鹏.人工骨生物材料的研究进展[J].临床骨科杂志, 2007,10(4):366-369.
[8] 崔文岗,石岩,肖德明.硫酸钙人工骨修复骨缺损的应用研究进展[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2013,10(5):21-23.
[9] 黄金龙,夏虹.去抗原异种骨的制备及复合异种骨的研究进展[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2012,4(3):227-232.
[10] 闵理.异种骨移植修复大段骨缺损的研究进展[J].中国骨与关节外科,2011,4(2):169-173.
[11] 高春阳,姜宏春,金春明.脱蛋白松质骨作为异种骨移植材料的修复作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(25): 4661-4664.
[12] Pape HC, Evans A, Kobbe P. Autologous bone graft: properties and techniques. J Orthop Trauma. 2010;24(Suppl1):36-40.
[13] Finkemeier CG.Bone-grafting and bone graft substitutes.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84-A(3):454-464.
[14] 邱贵兴,孙世荃.同种异体骨植入材料的临床应用[J].中华骨科杂志,2004,24(10);635-637.
[15] Nandi SK,Roy S,Mukherjee P,et al.Orthopaedic application of bone graft & graft substitutes: a review.Indian J Med Res. 2010;132:15-30.
[16] Turner TM,Urban RM,Gitelis S,et al.Resorption evaluation of a large bolus of calcium sulfate in a canine medullary defect.Orthopedics.2003;26(5 Suppl):577-579.
[17] Walsh WR,Morberg P,Yu Y,et al.Response of a calcium sulfate bone graft substitute in a confined cancellous defect.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2003; (406):228-236.
[18] 杨二平,彭昊,胡冰,等.医用硫酸钙人工骨与同种异体骨修复良性骨肿瘤骨缺损的对比分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2012, 16(34):6293-6297.
[19] 杨勇昆,徐海荣,牛晓辉.硫酸钙人工骨填充良性骨肿瘤刮除后骨缺损愈合情况的临床研究[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志, 2011,3(4):251-255.
[20] Schindler OS,Cannon SR,Briggs TW,et al. Use of a novel bone graft substitute in peri-articular bone tumours of the knee.Knee.2007;14(6):458-464.
[21] Ogose A,Hotta T,Kawashima H,et al.Comparison of hydroxyapatite and b-tricalcium phosphate as bone substitute after excision of bone tumours.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2005;72:94-101.
[22] Kelly CM,Wilkins RM,Gitelis S,et al.The use of a surgical grade calcium sulfate as a bone graft substitute: results of a multicenter trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2001;(382):42-50.
[23] 吴祖尧.诱导成骨与骨形态发生蛋白[J].中华骨科杂志, 1988, 8(3): 231-234.
[24] 刘玮,胡蕴玉,陆裕朴,等.重组合异种骨的研制及其生物活性分析[J].中华医学杂志,1991,71(7):378-380.
[25] 胡蕴玉,陆裕朴,刘伟,等.重组合异种骨的实验研究和临床应用[J].中华外科杂志, 1993,31(12):709-713.
[26] 于忠英,袁志,张伟.重组合异种骨替代自体骨治疗骨不连的长期疗效观察[J].科学技术与工程,2012,12(25):6281-6285.
[27] 赵清.重组合异种骨材料修复颌骨囊肿术后骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(19):3751-3753.
[28] Bucholz RW. Nonallograft osteoconductive bone graft substitutes. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2002;(395):44-52.
[29] Bakhtiari L,Rezaie HR,Hosseinalipour SM,et al. Investigation of biphasic calcium phosphate/gelatin nanocomposite scaffolds as a bone tissue engineering. Ceram Int.2010;36:2421-2426. |